Air source heat pumps
Air source heat pumps use the energy in outside air or air from a ventilation system for heating, cooling and heating water. They can be installed entirely inside or outside the house. Or, you can have a system with one unit inside the building and one outside.
Water source heat pumps
Water source heat pumps use the energy stored in ground water, surface, or sea or sewage water. The heat pump takes heat from the water and makes it available for heating, cooling and preparation of hot water. Water source heat pumps are particularly efficient because water is a very good energy carrier.
Ground source heat pumps
Ground source heat pumps use the energy stored in the ground. They extract heat from the ground either by a vertical or horizontal collector.
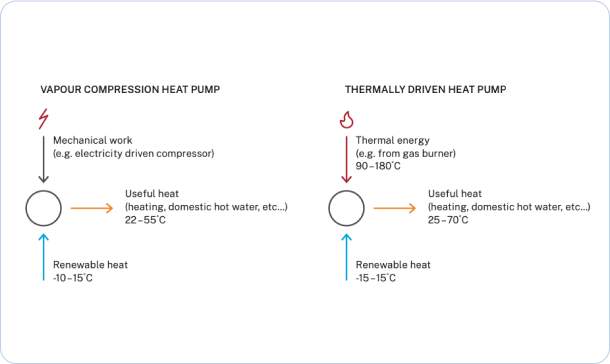
Electrically and thermally driven heat pumps
Many heat pumps use electricity to drive the compression cycle – meaning to heat up the energy from the air, water or underground a bit more. The heat pump can be plugged in and use renewable electricity.
Thermally driven heat pumps use heat or an engine to drive the compression cycle instead.
There are three main types of thermally driven heat pumps. Gas sorption heat pump (GAHP) and thermal compression heat pump (TCHP) are both covered by the standard EN 12309 and gas engine heat pump (GEHP) is covered by the standard EN 16905.